Trust-Supporting Design Features for Customer Service Chatbots
Olivia Bruhin • April 10, 2021
Introduction
Based on recent advantages in the area for artificial intelligence (AI), chatbots play a crucial role in customer service. However, due to a lack of user trust in chatbots, the adaption of the technology in the business are is only progressing slowly. The paper by Zierau, N., Hausch, M., Bruhin, O., & Söllner, M. (2020) serves as an initial identification of possible design principles to support trust in chatbots in the customer service domain.
Why Design Principles Support Trust in Chatbots
As an automated communication software powered by artificial intelligence, chatbots work as an interactive information partner. They enable users to experience fast and seamless humanlike conversations in natural language. On the company-side, chatbots represent a high-quality and cost-effective method for dealing with recurring and standardized inquiries to improve customer service. However, due to a lack of trust in AI, the widespread adaptation of the technology is still lacking in spite of the wide range of possible applications in the business field (Griffeth and Simonite 2018). Scholars observed that one reason for this might be that the development and adaption of chatbots in the business area was initially based on technology push rather than market pull. This resulted in a failure of sufficiently identifying customer pains and subsequently addressing customer needs and wishes (Coniam 2014). To address these shortcomings, Dietrich et al. (2019) mentioned the importance of standardizing design principles that support trust in chatbots as well as evaluating their instantiation.
In order to do so, the development of the design principles was carried out step by step according to the Design Science Research Approach by Hevner (2007) using a mixed-method approach (mix of qualitative and quantitative evaluation).
How to Develop Trust-Supporting Design Principles for Chatbots
First, findings from 22 semi-structured qualitative user and expert interviews were summarized in 12 user stories. These provided an initial, qualitative overview of elements relevant for the development of trust in interactions with text-based digital assistants.
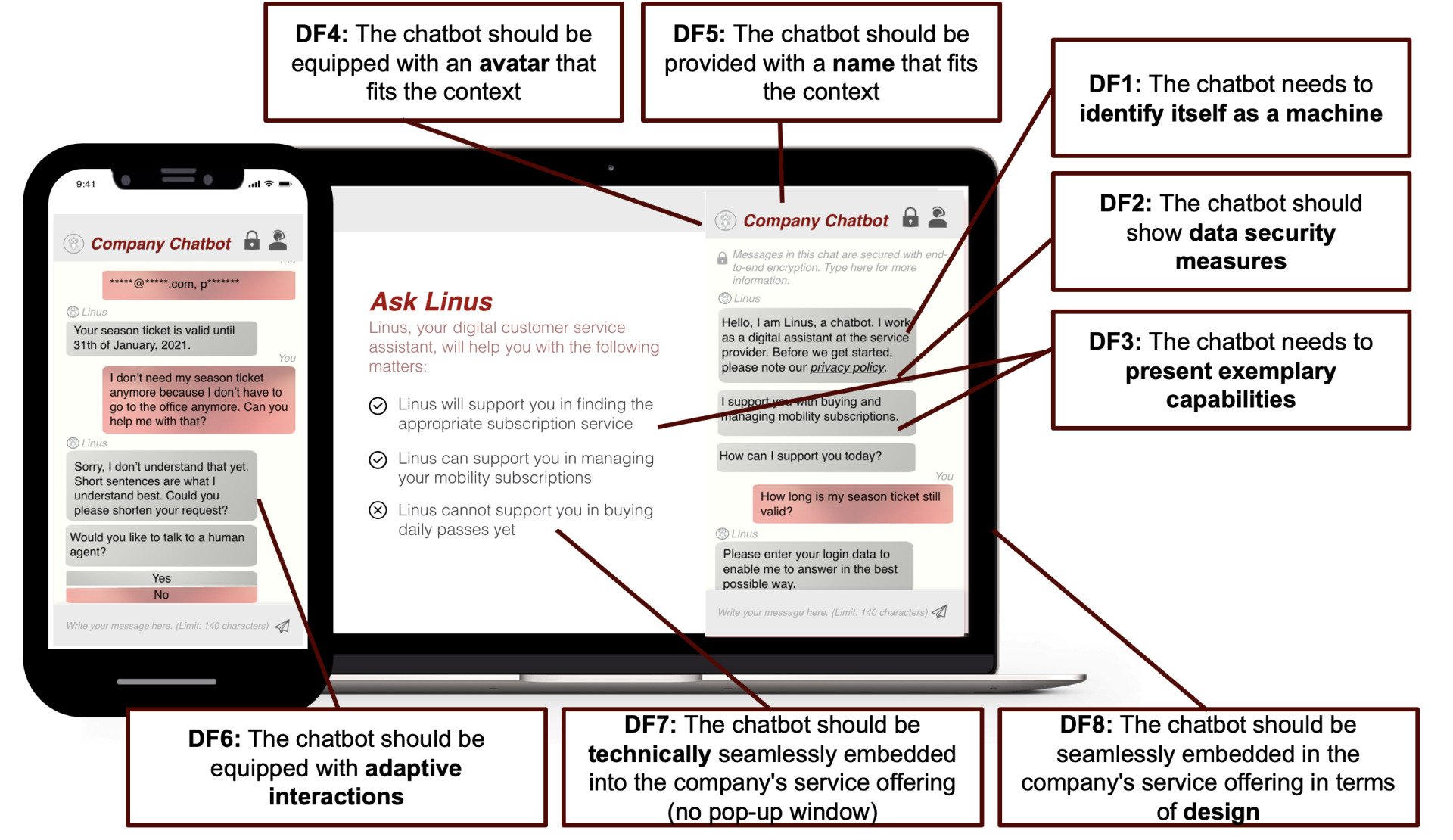
Second, an extended systematic literature review was carried out and revealed that trust in chatbots can be divided into trust in chatbot, environment and user-related criterias which include different trust-relevant components. From the considered literature, 10 literature issues are identified which are integrated into meta-requirements. The meta-requirements describe which requirements are to be built into the artifact. In the final step of the development, design principles are being created. Following a specific formulation, they define the concrete implementation of the previously defined meta-requirements in the artifact. Finally, design features represent the lowest granular level of design elements and the eight identified can be seen in the figure in this article. As components of design principles, they define exactly how which element from the proposed artifact can be implemented in a concrete use case.
The 8 Design Principles to Implement Chatbots in Customer Service
In conclusion, the following eight design principles are recommended to implement in chatbots for customer service:

Olivia Bruhin
Master Student in Business Innovation at the University of St. Gallen (HSG) and HCI-Enthusiast
After finishing her bachelor's degree in business administration, economics and psychology at the University of Berne, Olivia gained work experience in innovation management at SBB CFF FFS AG and PostFinance. To deepen the knowledge in this field, she started her master's degree in business innovation at the University of St.Gallen (HSG) in fall 2019. There, she mainly focuses on corporate entrepreneurship, design thinking as well as applications in the field of human-computer interaction with a special interest in the healthcare sector.
Need support with your Generative AI Strategy and Implementation?
🚀 AI Strategy, business and tech support
🚀 ChatGPT, Generative AI & Conversational AI (Chatbot)
🚀 Support with AI product development
🚀 AI Tools and Automation


What is AI Cybersecurity and what is Security for AI? AI cybersecurity is the use of artificial intelligence to protect IT systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. detect attacks and anomalies in logs and traffic, identify phishing, malware, and fraud, prioritize and respond to security incidents faster than humans can.

Should I use several AI tools or stick to one platform? That's a question I often hear from clients. 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐫𝐞𝐚𝐥 𝐚𝐧𝐬𝐰𝐞𝐫? 𝐈𝐭 𝐝𝐞𝐩𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐬 𝐨𝐧 𝐲𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐮𝐬𝐞 𝐜𝐚𝐬𝐞. Ask yourself: What problem are you trying to solve? Our guideline to be successful with your AI tool journey 1. Start by exploring a few major large language model platforms (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, etc.). - Gemini -> Amazing multimodality, images - ChatGPT -> Swiss Knife for AI, great for coding, logical and analytical tasks. - Claude -> Psychological, enhanced writing and strong with coding 2. Once you’ve defined your use case, commit to one main tool and consider upgrading to a paid version for the full experience. Still continue experimenting with specialised tools for certain tasks, so you learn, get ideas and can depriorize certain use cases. 3. Most importantly, invest in learning prompt engineering and focus on solving real problems that deliver value for you or your business and your clients. Sometimes, you don’t even need AI!

AI-powered chatbots, whether developed in-house or deployed through trusted platforms, are revolutionizing customer service, knowledge access, and internal communication. However, alongside these opportunities come new legal obligations: data protection , transparency , and EU AI Act compliance must be addressed carefully. This article covers: Where AI chatbots bring business value What compliance risks you must manage How to implement AI chatbots successfully and securely

Since August 2024, users have been able to use the web version of the image creation tool Midjourney. This simplifies usage by providing a user-friendly interface to experiment with one of the top Generative AI image creation tools available. We tested it for you and are sharing helpful tips and tricks. How to prompt images with Midjourney? If you use Midjourney on discord, there is a clear prompt structure and prompt parameters to adhere to. Usually, it makes sense to stick to it: 1) To prompt use "/Imagine" 2) Then enter your subject (description and details) you want to see on the image and it's environment (see yellow highlighted below in the prompt example) 3) Then enter composition, lightning, colours (see green highlighted below in the prompt example) 4) Finally add technical parameters to adjust and finalize your image. Please find a useful parameter library here.